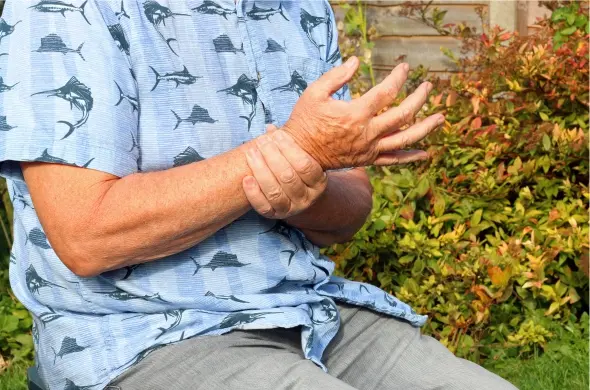
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing over 100 different types of joint inflammation or joint disease and related diseases. Understanding arthritis is crucial for recognizing its impact on daily life and seeking effective ways to manage and treat the condition. This article delves into the definition of arthritis, its symptoms, types, prevention strategies, management techniques, treatment options, natural remedies, and the importance of a healthy lifestyle for arthritis patients.
1. Definition of Arthritis
Arthritis is a term derived from the Greek words “arthro” (joint) and “itis” (inflammation). It refers to the inflammation of one or more joints, resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement. While commonly associated with aging, joint inflammation can affect individuals of all ages, including children.
2. Arthritis Symptoms
The symptoms of joint inflammation can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common joint disease symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, redness, and a decreased range of motion. These symptoms can be intermittent or chronic, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
3. Types of Arthritis
Joint diseases, often referred to as arthropathies, encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the joints, including:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common form of joint inflammation, OA is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the synovium (lining of the membranes that surround the joints), causing inflammation, pain, swelling, and eventually joint deformity.
- Gout: A type of joint inflammation caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling, often starting in the big toe.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Associated with psoriasis, this inflammatory joint disease can affect any joint and is characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation of the vertebrae, which can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort. In severe cases, it can lead to the fusion of the spine.
- Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SLE): An autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling.
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA): The most common type of arthritis in children under the age of 16, characterized by persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Septic Arthritis: An infection in a joint, often caused by bacteria, which leads to severe pain, swelling, and redness. It is a medical emergency requiring prompt treatment.
- Reactive Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints triggered by an infection in another part of the body, often the intestines, genitals, or urinary tract.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (small sacs filled with fluid that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints), often due to repetitive motion or prolonged pressure.
4. Arthritis Prevention
While some forms of joint inflammation are unavoidable due to genetic factors, certain lifestyle changes can help in arthritis prevention:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on weight-bearing joints.
- Regular Exercise: Keeps joints flexible and strengthens muscles around them.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce joint disease symptoms.
- Avoiding Joint Injuries: Protective gear and caution can prevent joint damage during activities.
5. Arthritis Management
Effective arthritis management involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help control symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises can improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps patients adapt daily activities to ease joint stress.
- Assistive Devices: Canes, splints, and other devices provide support and reduce strain on joints.
6. Joint Inflammation Treatment Options
Joint Disease treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
- Medications: As mentioned earlier, various drugs can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Surgery: Joint replacement or repair may be necessary in severe cases.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections can provide temporary relief.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care may offer additional symptom relief.
7. Natural Remedies for Joint Disease
Many individuals seek natural remedies for arthritis to complement conventional treatments:
- Herbal Supplements: Turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Exercise: Gentle activities like yoga and swimming can help maintain joint flexibility.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Dietary Changes: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help manage symptoms.
8. Joint Disease Pain Relief
Effective arthritis pain relief can significantly improve quality of life. Strategies include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and prescribed medications.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint function.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Meditation, deep breathing, and biofeedback can help manage pain.
9. Healthy Lifestyle for joint inflammation
A healthy lifestyle for joint inflammation patients is vital in managing the condition and enhancing overall well-being:
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are beneficial.
- Balanced Diet: Emphasizing whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Weight Management: Maintaining an appropriate weight to reduce joint stress.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient sleep and rest to allow the body to heal.
- Stress Management: Techniques like mindfulness and relaxation exercises can help manage stress and reduce flare-ups.
10. Conclusion
Understanding joint inflammation is the first step in managing this complex and often debilitating condition. By recognizing the symptoms, exploring various types, and adopting effective prevention and management strategies, individuals can lead a healthier, more active life despite joint diseases. Combining conventional treatments with natural remedies and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can offer comprehensive relief and improve overall quality of life for those living with joint disease.
10 Key Factors for understanding Arthritis, Definition, Symptoms, Types, Prevention, Management, Treatment, and Healthy Lifestyle
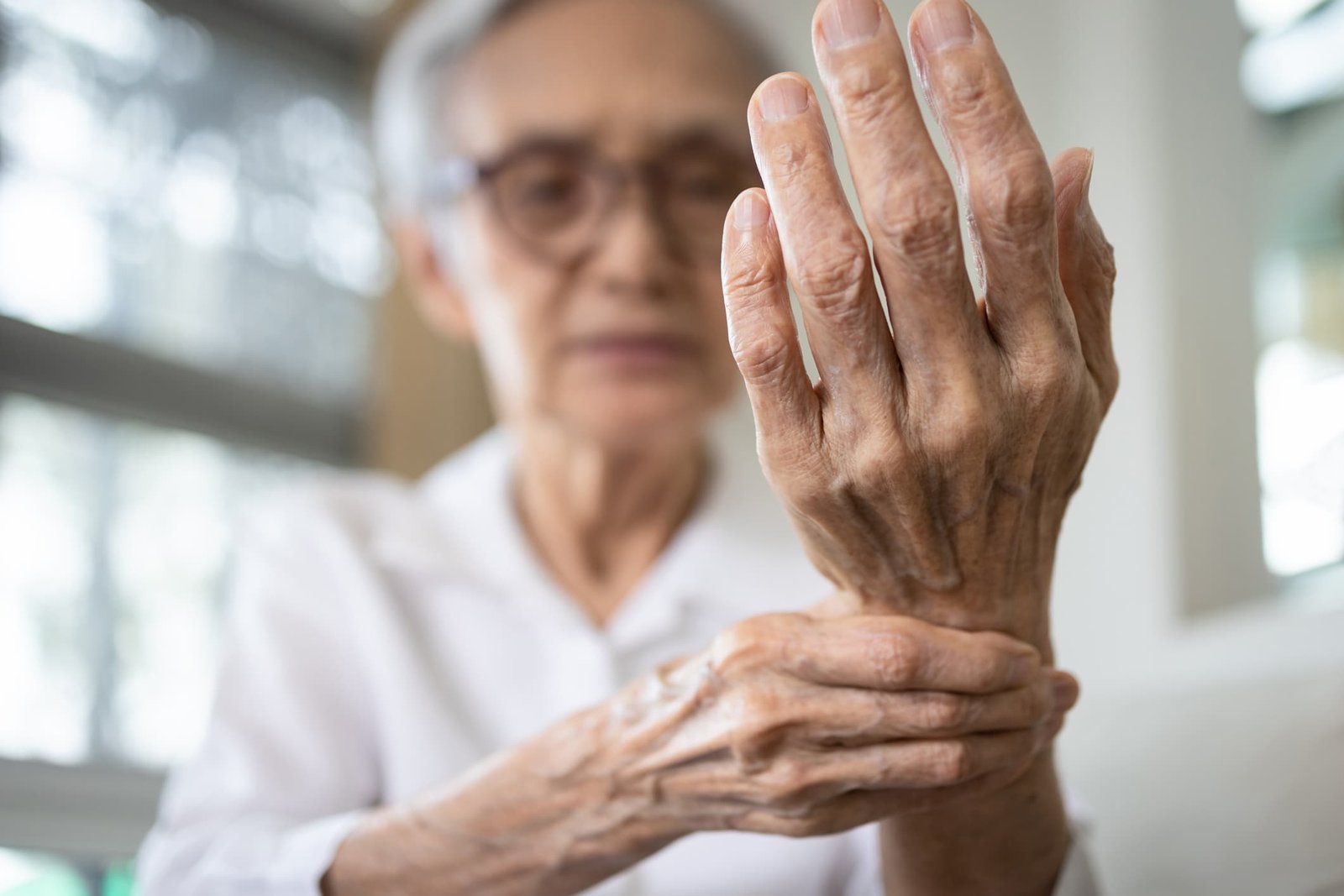
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing over 100 different types of joint inflammation or joint disease and related diseases. Understanding arthritis is crucial for recognizing its impact on daily life and seeking effective ways to manage and treat the condition. This article delves into the definition of arthritis, its symptoms, types, prevention strategies, management techniques, treatment options, natural remedies, and the importance of a healthy lifestyle for arthritis patients.
1. Definition of Arthritis
Arthritis is a term derived from the Greek words “arthro” (joint) and “itis” (inflammation). It refers to the inflammation of one or more joints, resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement. While commonly associated with aging, joint inflammation can affect individuals of all ages, including children.
2. Arthritis Symptoms
The symptoms of joint inflammation can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common joint disease symptoms include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, redness, and a decreased range of motion. These symptoms can be intermittent or chronic, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
3. Types of Arthritis
Joint diseases, often referred to as arthropathies, encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the joints, including:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common form of joint inflammation, OA is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the synovium (lining of the membranes that surround the joints), causing inflammation, pain, swelling, and eventually joint deformity.
- Gout: A type of joint inflammation caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling, often starting in the big toe.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Associated with psoriasis, this inflammatory joint disease can affect any joint and is characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing inflammation of the vertebrae, which can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort. In severe cases, it can lead to the fusion of the spine.
- Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SLE): An autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling.
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA): The most common type of arthritis in children under the age of 16, characterized by persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Septic Arthritis: An infection in a joint, often caused by bacteria, which leads to severe pain, swelling, and redness. It is a medical emergency requiring prompt treatment.
- Reactive Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints triggered by an infection in another part of the body, often the intestines, genitals, or urinary tract.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (small sacs filled with fluid that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near the joints), often due to repetitive motion or prolonged pressure.
4. Arthritis Prevention
While some forms of joint inflammation are unavoidable due to genetic factors, certain lifestyle changes can help in arthritis prevention:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on weight-bearing joints.
- Regular Exercise: Keeps joints flexible and strengthens muscles around them.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce joint disease symptoms.
- Avoiding Joint Injuries: Protective gear and caution can prevent joint damage during activities.
5. Arthritis Management
Effective arthritis management involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help control symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises can improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps patients adapt daily activities to ease joint stress.
- Assistive Devices: Canes, splints, and other devices provide support and reduce strain on joints.
6. Joint Inflammation Treatment Options
Joint Disease treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include:
- Medications: As mentioned earlier, various drugs can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Surgery: Joint replacement or repair may be necessary in severe cases.
- Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections can provide temporary relief.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care may offer additional symptom relief.
7. Natural Remedies for Joint Disease
Many individuals seek natural remedies for arthritis to complement conventional treatments:
- Herbal Supplements: Turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Exercise: Gentle activities like yoga and swimming can help maintain joint flexibility.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Dietary Changes: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help manage symptoms.
8. Joint Disease Pain Relief
Effective arthritis pain relief can significantly improve quality of life. Strategies include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and prescribed medications.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint function.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Meditation, deep breathing, and biofeedback can help manage pain.
9. Healthy Lifestyle for joint inflammation
A healthy lifestyle for joint inflammation patients is vital in managing the condition and enhancing overall well-being:
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are beneficial.
- Balanced Diet: Emphasizing whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Weight Management: Maintaining an appropriate weight to reduce joint stress.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient sleep and rest to allow the body to heal.
- Stress Management: Techniques like mindfulness and relaxation exercises can help manage stress and reduce flare-ups.
10. Conclusion
Understanding joint inflammation is the first step in managing this complex and often debilitating condition. By recognizing the symptoms, exploring various types, and adopting effective prevention and management strategies, individuals can lead a healthier, more active life despite joint diseases. Combining conventional treatments with natural remedies and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can offer comprehensive relief and improve overall quality of life for those living with joint disease.